Global energy demand is rising at a breathtaking pace – driven by the rapid development of artificial intelligence. More and more data centers are consuming enormous amounts of electricity, posing new challenges even for tech giants. Against this backdrop, Google is pushing ahead with the reactivation of the Duane Arnold Energy Center in Iowa. The technology company is thus relying on nuclear power to ensure a continuous supply of energy for its cloud and AI technologies. This planned recommissioning of the nuclear power plant is considered a strategic step towards a stable and climate-friendly energy supply. (ntv: 28.10.25)
Reactivating old infrastructure as part of the energy future
The Duane Arnold Energy Center, a nuclear power plant shut down in 2020, is central to these plans. Together with the energy company NextEra Energy, Google is preparing for its reactivation. Both partners aim to bring the plant back online by 2029. The goal is to meet the ever-growing electricity demands of AI systems in the long term.
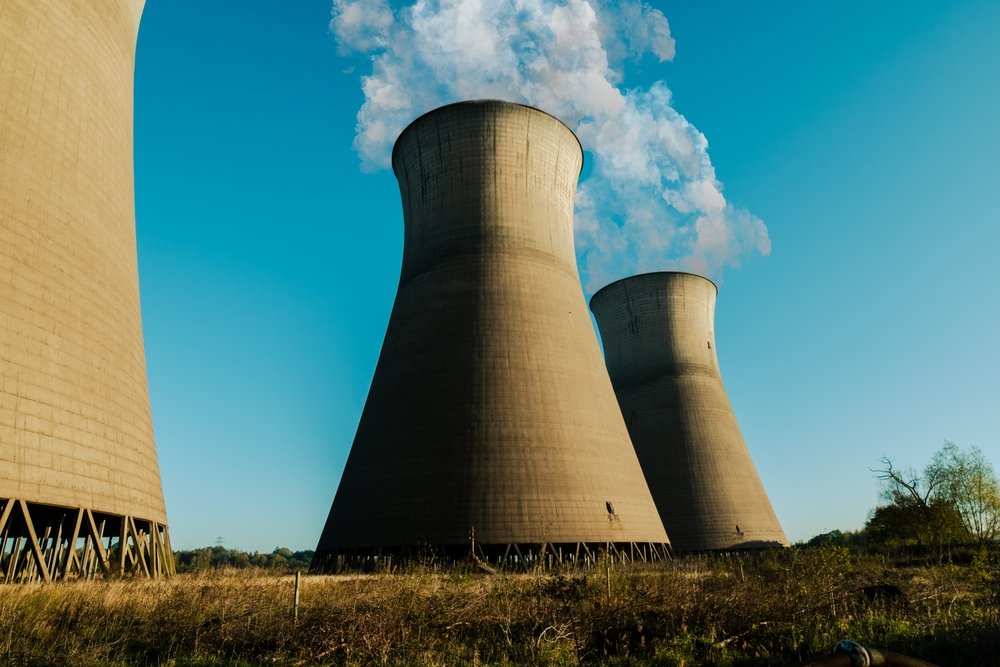

A contract for the purchase of energy for the next 25 years secures the cooperation. According to the companies, the collaboration is intended to enable sustainable expansion. Nuclear energy is considered a CO₂-free energy source and offers stability where wind and solar power reach their limits.
Artificial intelligence is driving the energy demand
With each new algorithm, energy consumption continues to rise. The International Energy Agency expects global electricity demand from data centers to double by 2030. The reason lies in the enormous computing power required by AI technology, which processes billions of data points in seconds.
To meet this increasing energy demand, tech companies are resorting to pragmatic solutions. Google is focusing on reactivating old power plants to combine security of supply with sustainability. The company is thus responding to the trend that green energy sources alone can no longer satisfy the global energy hunger of the digital economy.
Microsoft and Meta are following similar strategies
Other companies are also recognizing the value of recommissioning old reactors. Microsoft plans to obtain electricity from the decommissioned Three Mile Island nuclear power plant, which became world-famous due to an accident in the 1970s. Meta, the parent company of Facebook, has secured the energy production of a nuclear power plant in Illinois for 20 years.
These steps show a clear direction: the technology sector is once again relying on nuclear power to secure the energy supply for its digital infrastructure. The technology company Google is joining this trend – not out of nostalgia, but out of necessity.
Small Reactors as a Model for the Future
In addition to reactivating large power plants, Google plans to obtain energy from newly developed reactors from Kairos Power starting in 2030. These so-called “Small Modular Reactors” are considered safe, compact, and efficient. They can be placed closer to data centers, thus offering a flexible supplement to the existing energy supply.
Such innovations are intended to help satisfy the enormous energy demands of AI technology while simultaneously reducing environmental impact. The technology company sees this as a crucial step towards independence from fossil fuels.
Between Progress and Risk
The return to nuclear power remains controversial. Proponents see it as a necessary bridging technology for the digital future, while critics warn of unresolved issues regarding waste disposal and safety standards. However, given the exploding energy demand of artificial intelligence, reactivating old power plants appears to many as a realistic approach.
One thing is certain: With the recommissioning of the Duane Arnold Energy Center, Google is embarking on a course that carries symbolic significance. The company is combining digital innovation with traditional energy generation – a sign that the future of AI technology lies not only in algorithms but also in stable power sources.