A burning electric car has completely destroyed a two-family house near the Hessian city of Fulda. The resulting damage amounts to several hundred thousand euros. The house is uninhabitable. The tragic thing is that the fire brigade had to watch helplessly as the house burned down, because the solar system on the roof made it practically impossible to extinguish the fire.
Two-family house completely destroyed by burning electric car
According to the report of the East Hesse police headquarters, the two-family house affected is uninhabitable due to the fire. The adjacent garage and another vehicle were also completely destroyed by the fire in the electric car. According to the police report, residents and neighbours were awakened during the night by a loud bang. The fire-fighting efforts proved difficult. First, a specialised salvage company had to remove the burning electric car from the garage. Afterwards, the burning electric car was transported to an extinguishing basin to smother the fire. It is not yet clear why the electric car caught fire. According to unconfirmed reports, it was an Audi e-tron.
Solar system on the roof complicates extinguishing work
Despite a fire brigade of 50 firefighters from various villages in the vicinity, the fire spread to the adjacent two-family house. The solar system on the roof made the fire-fighting efforts very difficult, so that the house burned down completely. When such systems catch fire, the fire brigade must always keep a safe distance to avoid the risk of electrocution. The risk of electrocution also severely restricts the use of extinguishing agents.
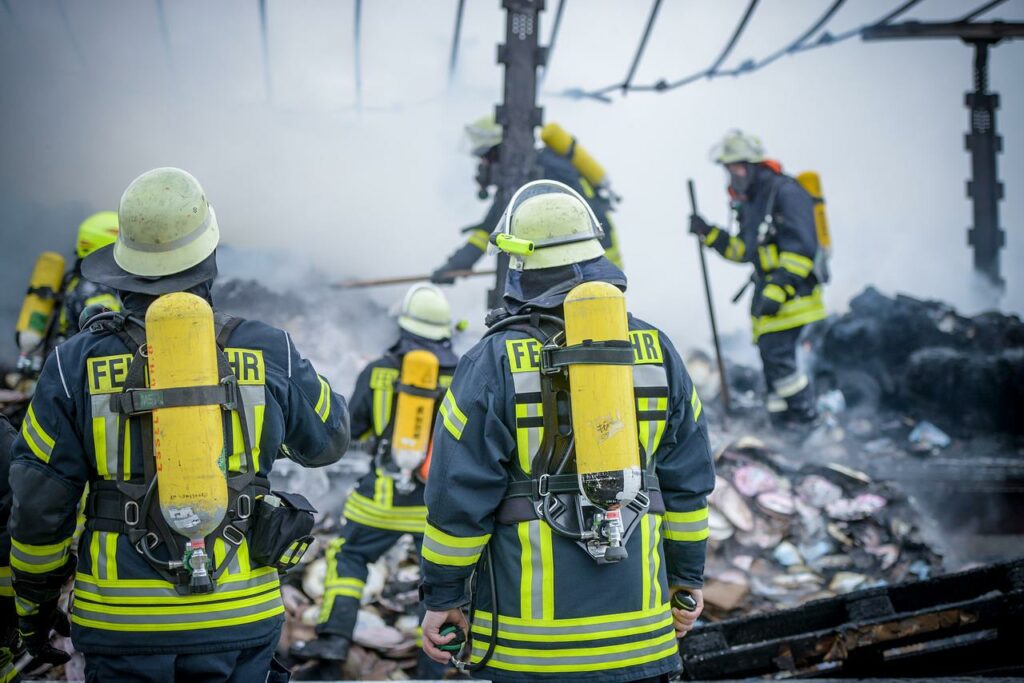

Burning lithium-ion batteries repeatedly cause fires in homes. Burning solar storage batteries have already completely destroyed three residential buildings. Also, batteries from electric bicycles or small appliances also repeatedly lead to fires that are difficult to extinguish.
Extinguishing lithium-ion batteries is difficult
Lithium-ion batteries can be exposed to high temperatures during charging. If this causes damage to the layer structure of the metal oxides used, a thermal reaction can occur. High amounts of energy are released and elemental oxygen is formed. With the high heat input, the electrolyte liquid evaporates and easily combustible gases are formed.
As soon as these gases ignite, the lithium-ion cell burns. The fire of the first cell triggers a self-reinforcing process that is difficult to stop. Since the battery housings are usually thermally insulated, extinguishing water usually does not reach the source of the fire. A battery fire can therefore only be extinguished by external cooling. However, this requires enormous amounts of water.